December 21, 2016 at 1:51 PM
Print Buyer's Quick Guide to Vector vs. Raster
Your printer just told you the art file you provided has some issues and you have been asked if you can provide a vector file. When you questioned what that means you received a response from your printer that didn’t help you understand the problem any clearer. Now you’re frustrated and feel like sending your business to another printer. Unfortunately, another printer will either tell you the same thing or will produce your piece with unsatisfactory results. The print quality of your project largely depends upon the type of files you provide, and in commercial printing not all file types are equal. Here is a quick guide to help you understand the difference between Vector files and Raster files.
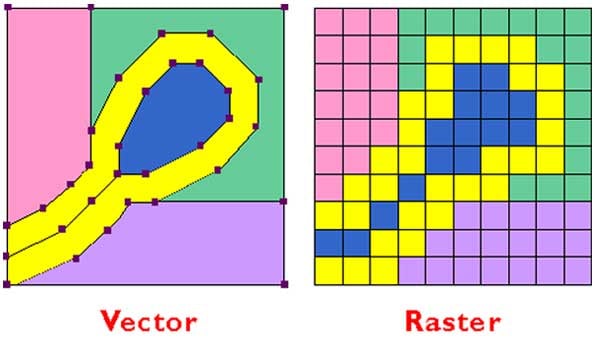 Raster images are produced as a pattern of pixels. Each pixel is a tiny square assigned a color. The pixels are arranged in rows and columns on a map, each pixel in a fixed place. When displayed together they form an image. Raster is the standard image format for computer graphics and digital cameras. Raster images have defined proportions based on their resolution. If you attempt to enlarge a low resolution raster image the image will distort and become pixelated, appearing blocky and blurry.
Raster images are produced as a pattern of pixels. Each pixel is a tiny square assigned a color. The pixels are arranged in rows and columns on a map, each pixel in a fixed place. When displayed together they form an image. Raster is the standard image format for computer graphics and digital cameras. Raster images have defined proportions based on their resolution. If you attempt to enlarge a low resolution raster image the image will distort and become pixelated, appearing blocky and blurry. 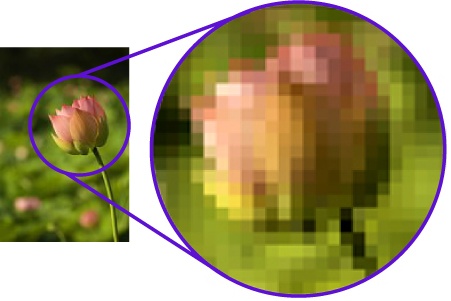 To give you an idea of how many pixels make up an image, an 8 megapixel camera captures images digitally composed of 8 million pixels. Digital photographs comprised of millions of pixels have the ability to produce an image with extremely fine detail, with each pixel assigned any of 16 million colors. In terms of resolution, dpi (dots per inch) or ppi (pixels per inch) indicate the density of the pixels comprising the image. A 72 dpi is low resolution and most commonly used on websites. If you want to digitally print your image it should be 600 dpi or higher. Laser printers typically print up to 1,200 dpi. The most common raster image file extensions are:
To give you an idea of how many pixels make up an image, an 8 megapixel camera captures images digitally composed of 8 million pixels. Digital photographs comprised of millions of pixels have the ability to produce an image with extremely fine detail, with each pixel assigned any of 16 million colors. In terms of resolution, dpi (dots per inch) or ppi (pixels per inch) indicate the density of the pixels comprising the image. A 72 dpi is low resolution and most commonly used on websites. If you want to digitally print your image it should be 600 dpi or higher. Laser printers typically print up to 1,200 dpi. The most common raster image file extensions are:
.jpg (.jpeg) - Joint Photographic Experts Group
JPG files are by far the most common image files produced by digital cameras and one of the most common file types found on the internet. If you are viewing pictures online you are most likely looking at JPGs. If you try to print a JPG on a colored sheet of paper you will notice the image is in a white box. JPG does not support a transparent background. JPG files will loose resolution when you enlarge the size.
.gif - Graphics Interchange File
GIFs are commonly used in simple animations. Animated GIFs have become very popular on social media and the web. Most animated GIFs have a short duration of a few seconds.
.png - Portable Network Graphic
PNG has one big advantage. PNG files support transparent backgrounds.
.psd - Adobe Photoshop Document
PSDs are produced when images edited in Photoshop are saved. Photoshop is the industry standard for complex manipulation of photos.
.tif (.tiff) - Tagged Image File Format
TIFs are large raster files and are lossless, which means they can be scaled larger without losing resolution. TIFs are good for printing photographs.
Vector Art is also called Line Art. Vector images are built from polygons, lines between two points using geometric mathematical formulas. The lines are plotted along an X and Y axis and can be straight or curved. For example, a line could appear as a circle, or a triangle, or take on any number of attributes. Vector graphics are the standard format for commercial printing. Vector files can be manipulated easily, widened, lengthened, compressed, or expanded without losing resolution. The image is not restricted by size or shape. The same image used on a postcard could also be used on a poster or e ven a billboard. Vector images can also be easily converted into raster, which in fact is necessary to view a vector image on a computer display or print your image on your desktop printer. This conversion is called rasterization.
ven a billboard. Vector images can also be easily converted into raster, which in fact is necessary to view a vector image on a computer display or print your image on your desktop printer. This conversion is called rasterization.
The most common file extensions include:
.ai - Adobe Illustrator Graphics File
Professional Creative Services design original artwork primarily in Adobe Illustrator, which has become established as the industry standard and is the program most often taught in design schools.
.eps - Encapsulated PostScript File
EPS is the most common file type for use in commercial printing. EPS supports high resolution graphics. Vector based software is required in order to view EPS files.
.pdf - Portable Document Format
PDF is the most common file format for sharing documents and graphics. PDFs can be opened and viewed by numerous different software programs. Adobe Acrobat Reader is almost universally used as the free PDF viewing program of choice, but there are many others available. There are also many programs which allow saving a file as a PDF. The downside to PDFs is they are not easy to edit or manipulate. Commercial printers can produce high quality print from PDFs, but you need to supply your printer with a print-ready PDF, meaning it requires no alterations.
There are many different software programs available to businesses and consumers for graphic design and publishing. If your printer has told you there is an issue with your art file you most likely provided a low resolution JPG. If you are supplying graphics, such as a company logo, you should supply it as an EPS file or a PDF. Most commercial printers will work with whatever you’re able to furnish. There are software programs available which convert raster images to vector, but the quality of the converted image is usually questionable and often requires additional editing, which can be time consuming and potentially expensive. The best option is to ask your designer to supply you with multiple different file types for use in a variety of applications.
Popular Posts

Memorial Weekend

Landing Pages
Learn Why Omnichannel Marketing is Trending

Direct Mail




